4CzIPN-tBu
CAS Number 1630263-99-8
Dopant Materials, Materials, OLED Materials, Semiconducting Molecules,A TADF yellow emitter, assistant host and photocatalyst
Used as an assistant dopant for highly efficient hyperfluorescent or as solo emitter for TADF devices.
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
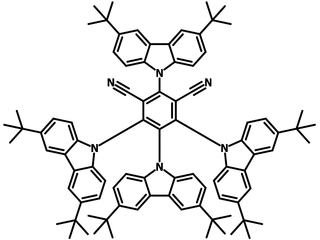
4CzIPN-tBu (CAS number 1630263-99-8), also known as 2,4,5,6-tetrakis(3,6-di-tert-butylcarbazol-9-yl)-1,3-dicyanobenzene, a donor-acceptor type molecule composed of dicyanobenzene and tert-butyl-substituted carbazolyl groups around the benzene ring.
4CzIPN-tBu is slightly red-shifted in absorption while comparing to that of 4CzIPN as the eight tert-butyl groups improve the donor strength of the carbazole units thus altering the donor–acceptor interaction. Also, due to the bulkier peripheral tert-butyl groups increasing steric effects, 4CzIPN-tBu experiences weaker intermolecular interactions in the solid-state.
Remarkably, the electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) efficiency of 4CzIPN-tBu in dichloromethane reached almost 40% and stable electrogenerated chemiluminescence was observed from 4CzIPN-tBu due to the fact that polymerization is inhibited by the steric hindrance of the bulky tert-butyl groups at 3,6-postion of the carbazoles.
Solution-processed hyperfluorescent devices with an external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 15.3% using cibalackrot as the fluorescent emitter and 4CzIPN-tBu as the TADF assistant host in CBP. These sterically hindered tert-butyl groups effectively reduced losses caused by triplet diffusion between the TADF assistant host and the fluorescent emitter by spatially separating adjacent molecules and making a concurrent frontier molecular orbital (FMO) less likely [1].
General Information
| CAS Number | 1630263-99-8 |
| Full Name | 2,4,5,6-Tetrakis(3,6-di-tert-butylcarbazol-9-yl)-1,3-dicyanobenzene |
| Synonyms | 4CzIPN-Bu, t4CzIPN, 2,4,5,6-Tetrakis(3,6-di-tert-butyl-9H-carbazol-9-yl)-1,3-benzenedicarbonitrile, 2,4,5,6-Tetrakis(3,6-di-tert-butyl-9H-carbazol-9-yl)isophthalonitrile |
| Chemical Formula | C88H96N6 |
| Molecular Weight | 1237.74 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 389 nm in film |
| Photoluminescence | λem 550 nm in film |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.70 eV, LUMO = 3.30 eV [1] |
| Classification / Family | Carbazole derivative, TADF materials, Yellow dopant materials, Sublimed materials |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Purity | Unsublimed >98.0% (1H NMR) |
| Melting Point | N/A |
| Appearance | Orange powder/crystals |
Device Structure(s)
| Device Structure | ITO (100 nm)/PEDOT:PSS (30 nm)/Cibalackrot:4CzIPN-tBu:mCBP (0.5:29.5:70 mol%, 35 nm)/TPBi (65 nm)/Liq (2 nm)/Al (100 nm) [1] |
| Color |
|
| Max. Brightness | 4595 cd/m2 |
| Max. EQE | 15.3% |
| Device Structure | ITO (100 nm)/PEDOT:PSS (30 nm)/4CzIPN-tBu:mCBP (30:70 mol%, 35 nm)/TPBi (65 nm)/Liq (2 nm)/Al (100 nm) [2] |
| Color |
|
| Max. Brightness | 15,700 cd/m2 |
| Max. EQE | 10.7% |
| Device Structure | ITO (100 nm)/PEDOT:PSS (30 nm)/6,6’-Cibalackrot:4CzIPN-tBu:mCBP (0.5:29.5:70 mol%, 35 nm)/TPBi (65 nm)/Liq (2 nm)/Al (100 nm) [2] |
| Color |
|
| Max. Brightness | 11,920 cd/m2 |
| Max. EQE | 10.7% |
| Device Structure | ITO (100 nm)/PEDOT:PSS (30 nm)/5,5’-Cibalackrot:4CzIPN-tBu:mCBP (0.5:29.5:70 mol%, 35 nm)/TPBi (65 nm)/Liq (2 nm)/Al (100 nm) [2] |
| Color |
|
| Max. Brightness | 12,440 cd/m2 |
| Max. EQE | 12.5% |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- High-performance solution-processed red hyperfluorescent OLEDs based on cibalackrot, N. Wallwork et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 10, 4767-4774 (2022); DOI: 10.1039/D1TC04937B.
- Cibalackrot Dendrimers for Hyperfluorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, N. Wallwork et al., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 43 (16), 2200118 (2022); DOI: 10.1002/marc.202200118.
-
Photophysical Properties and Efficient, Stable, Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence of Donor–Acceptor Molecules Exhibiting Thermal Spin Upconversion, R. Ishimatsu et al., Chem. Euro. J., 22 (14), 4889-4898 (2016); DOI: 10.1002/chem.201600077.
