2CzPN
CAS Number 1416881-50-9
Blue Dopant Materials, Dopant Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Materials,2CzPN, highly efficient TADF sky blue emitter
High-purity (>99.0%) and available online in sensible quantities for priority dispatch, 2CzPN, 1416881-50-9, 1,2-Bis(carbazol-9-yl)-4,5-dicyanobenzene
2CzPN is a highly efficient TADF sky blue emitter with two electron-donating carbazolyl moieties attached to the electron-withdrawing dicyanobenzene ring. The carbazolyl units are noticeably distorted from the dicyanobenzene plane by steric hindrance, leading to a small ΔEST of 0.09 eV.
When compared with 4CzIPN, 2CzPN has fewer carbazolyl groups which reduces its electron-donating ability and produces a shift of the emission maximum to shorter wavelength (473 nm).
General Information
| CAS number | 1416881-50-9 |
|---|---|
| Full name | 4,5-Bis(carbazol-9-yl)-1,2-dicyanobenzene |
| Chemical formula | C32H18N4 |
| Molecular weight | 458.51 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 380 nm in toluene |
| Fluorescence | λmax 473 nm in toluene |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.8 eV, LUMO = 3.0 eV; T1 = 2.5 eV |
| Synonyms | 1,2-Bis(carbazol-9-yl)-4,5-dicyanobenzene |
| Classification / Family | Blue emitting layer materials, Blue phosphorescent host materials, TADF materials. |
Product Details
| Purity | Sublimed > 99% (HPLC) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | Not available |
| Appearance | Pale yellow crystals/powder |
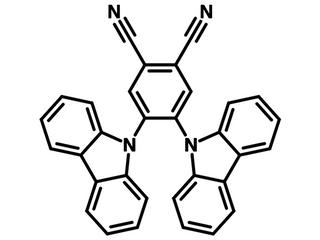
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3 (5 nm)/NPB (40 nm)/mCP (10 nm)/2CzPN: (tbt)2Ir(acac) (15 nm, 1.0 wt%)/Bphen (40 nm)/Mg: Ag (100 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Color | Orange |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 42.1 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 77.9 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 26.8% |
| Max. Luminance Efficiency | 119,900 cd/m2 |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT:PSS/PVK:2CzPN (20 wt%, 20 nm)/QDs/ZnO (40 nm)/Al [3] |
|---|---|
| Color | Red |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 13.77 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 17.33 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 12.37% |
| Device structure | ITO/TAPC (40 nm)/TCTA (20 nm)/DPSTPA* (75%):2CzPN (25%) (30 nm)/3TPYMB (80 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [4] |
|---|---|
| Color | Green |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 62.7 ± 2.2 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 59.9 ± 2.2 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 19.0 ± 0.6% |
| Device structure | ITO/HATCN (5 nm)/NPB (40 nm)/TCTA (10 nm)/mCP:6 wt% 2CzPN (11 nm)/TAZ:4 wt% PO-01 (4 nm)/TAZ (40 nm)/LiF (0.5 nm)/Al (150 nm) [5] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 80.1 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 47.1 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 38.4% |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT:PSS (40 nm)/TAPC (20 nm)/TCTA (5 nm)/o-CzCN:2CzPN (4 wt%, 20 nm)/TmPyPB (40 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (200 nm) [6] |
|---|---|
| Color | Blue |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 18.36 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 29.23 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 14.52% |
Pricing
| Grade | Order Code | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sublimed (>99% purity) | M2181A1 | 100 mg | £280 |
| Sublimed (>99% purity) | M2181A1 | 250 mg | £560 |
| Sublimed (>99% purity) | M2181A1 | 500 mg | £950 |
| Sublimed (>99% purity) | M2181A1 | 1 g | £1550 |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Highly efficient organic light-emitting diodes from delayed fluorescence, H. Uoyama et al., Nature, 492, 234-240 (2012); doi: 10.1038/nature11687.
- High-efficiency phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices with low efficiency roll-off using a thermally activated delayed fluorescence material as host, Y. Qi et al., Org. Electron., 36, 185-191 (2016); DIO: 10.1016/j.orgel.2016.05.043.
- Efficient Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Diodes Employing Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitters as Exciton Harvesters, Y. Zhang et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10, 7435−7441 (2018); DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b16579.
