DCJTB, one of the most promising dopant materials
Widely used in red and white OLEDs, 4-(Dicyanomethylene)-2-tert-butyl-6-(1,1,7,7-tetramethyljulolidin-4-yl-vinyl)-4H-pyran, CAS No. 200052-70-6, Unsublimed ≥98.0%
DCJTB, a dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran (DCM) derivative, is one of the most promising dopant materials. It has been widely used in red and white OLEDs.
With four methyl bulky substituents on the julolidine moiety, and tert-butyl group on the pyran moiety of DCM backbone structure, DCJTB can efficiently prevent concentration quenching between the emitting materials, which leads to improved device electroluminescence efficiencies.
DCJTB has also been used as an interface material between the dye and acceptor in small molecule organic heterojunction solar cells, retarding the charge recombination between the donor and the acceptor.
General Information
| CAS number | 200052-70-6 |
|---|---|
| Full name | 4-(Dicyanomethylene)-2-tert-butyl-6-(1,1,7,7-tetramethyljulolidin-4-yl-vinyl)-4H-pyran |
| Chemical formula | C30H35N3O |
| Molecular weight | 453.62 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 502 nm in THF |
| Fluorescence | λmax 602 nm in THF |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.4 eV, LUMO = 3.2 eV [1] |
| Synonyms |
|
| Classification / Family | Red dopant materials, OLED red emitters, TADF materials. |
* Measurable with an optical spectrometer
Product Details
| Purity | Unsublimed > 98.0% (HPLC) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | n/a |
| Appearance | Deep red crystals/powder |
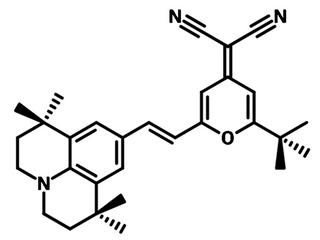
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3 (3 nm)/NPB (20 nm)/TCTA (8 nm)/TCTA:3P-T2T (1:1): 1 wt% DCJTB (15 nm)/3P-T2T (45 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al [1] |
|---|---|
| Color | Red |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 21.5 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 22.7 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 10.15% |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3 (3 nm)/mCBP (20 nm)/mCBP:PO-T2T:0.4 wt.% DCJTB (20 nm)/PO-T2T (40 nm)/LiF (0.8 nm)/Al [2] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 10.39 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 13.25 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 6.16% |
| Device structure | ITO/HAT-CN (10 nm)/TAPC (55 nm)/TCTA (10 nm)/TCTA:B4PyMPM:2 wt% 4CzIPN:0.5 wt% DCJTB (30 nm)/B4PYMPM (55 nm)/Liq (2 nm)/Al (110 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Color | Orange |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 26.3 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 23.0 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 12.3% |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT:PSS (35 nm)/26DCzPPy:TCTA:10 wt % DMAC-TRZ/1 wt % DCJTB (45 nm)/TmPyPB (50 nm)/CsF(1 nm)/Al [2] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 10.3 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 16.4 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 6.58% |
*For chemical structure information, please refer to the cited references
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Highly efficient red OLEDs using DCJTB as the dopant and delayed fluorescent exciplex as the host, B. Zhao et al., Sci. Rep., 5, 10697 (2015); DOI: 10.1038/srep10697.
- Simple structured hybrid WOLEDs based on incomplete energy transfer mechanism: from blue exciplex to orange dopant, T. Zhang et al., Sci. Rep., 5, 10234 (2015); DOI: 10.1038/srep10234.
- Triplet exciton harvesting by multi-process energy transfer in fluorescent organic light-emitting diodes, D. Li et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 7, 977 (2019); DOI: 10.1039/c8tc05141k.
