BCBP
CAS Number 858131-70-1
High Purity Sublimed Materials, Host Materials, Materials, OLED Materials,BCBP, host material for blue, green, red phosphorescent dopants for highly efficient OLED devices
High-purity (>99.0%) and available online for priority dispatch, BCBP, Sublimed ≥99%, CAS No. 858131-70-1
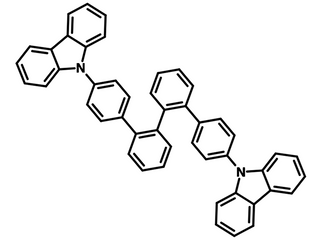
2,2'-bis(4-(carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)-biphenyl (BCBP) has a bridged biphenyl structure with two electron rich carbazolyl pendant moieties. The bridged structure is believed to enhance the conjugation and raise the HOMO energy level, facilitating hole-injection and leading to low turn-on voltages in organic photoelectroluminescent devices.
Comparing with 4,4′-(bis(9-carbazolyl))biphenyl (CBP), a well known host material, BCBP is thermally more stable with a high glass transition temperature (Tg) of 173 °C, while CBP has a relatively low Tg of 69 °C.
Carbazolyl groups are largely embedded in both fluorescent and phosphorescent host materials because of their higher triplet energy levels and higher hole mobility. Like the rest of the family members such as CDBP and mCBP, BCBP is commonly used as host material for blue, green, red phosphorescent dopants for highly efficient OLED devices.
General Information
| CAS number | 858131-70-1 |
|---|---|
| Full name | 2,2'-bis(4-(carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)-biphenyl |
| Chemical formula | C48H32N2 |
| Molecular weight | 636.78 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 325 nm in DCM |
| Fluorescence | λem 373 nm in DCM |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 6.1 eV, LUMO = 2.6 (Eg = 3.5 eV; ET = 2.8 eV) |
| Synonyms | 2,2'-bis(4-carbazolylphenyl)-1,1'-biphenyl |
| Classification / Family | Organic electronics, Hole transport layer materials (HTL), Fluorescent and phosphorescent host materials, TADF-OLEDs, Sublimed materials. |
* Measurable with a USB spectrometer
Product Details
| Purity | Sublimed* >99.0% (HPLC) |
|---|---|
| Melting point |
Tg = 173 °C (lit.) TGA: >330 °C (0.5% weight loss) |
| Color | White powder/crystals |
* Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals, see sublimed materials.
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/TPDPES:TBPAH (20 nm)/BTPD (20 nm)/BCBP:15%FIrpic (30 nm)/DPPS (30 nm)/LiF (0.5 nm)/Al (100 nm) [1] |
|---|---|
| Color | Blue |
| Max. Luminance | 10,578 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 50.5 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 22.0% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 47.0 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3/TAPC/Ir(dpm)(piq)2(4%):BSB/Eu(TTA)3Phen*(0.3%):Ir(dpm)(piq)2(4%):BCBP/TPBi/LiF/Al |
|---|---|
| Color | Red |
| Max. Luminance | 63,110 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 61.71 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 64.59 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3/TAPC/mer-Ir(Pmb)3(9%):BSB/Tm(acac)3Phen*(0.3%):mer-Ir(Pmb)3(9%):BCBP/TPBi/LiF/Al |
|---|---|
| Color | Blue |
| Max. Luminance | 20,095 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 30.08 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 37.56 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3/TAPC/Ir(ppy)2(m-bppy)(9%):Ir(piq)2(acac)(3%):BSB/Tm(acac)3Phen(0.3%):mer-Ir(pmb)3(25%):BCBP/TPBi/LiF/Al |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Luminance | 43,122 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 60.55 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 63.18 lm W-1 |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Nearly 100% Internal Quantum Efficiency in an Organic Blue-Light Electrophosphorescent Device Using a Weak Electron Transporting Material with a Wide Energy Gap, L Xiao et al., Adv. Mater., 21, 1271–1274 (2009); DOI: 10.1002/adma.200802034.
- Diarylmethylene-bridged 4,4′-(bis(9-carbazolyl))biphenyl: morphological stable host material for highly efficient electrophosphorescence, Z. Jiang et al., J. Mater. Chem., 19, 7661-7665 (2009); DOI: 10.1039/B910247G.
- Towards Highly Efficient Blue-Phosphorescent Organic Light-EmittingDiodes with Low Operating Voltage and Excellent Efficiency Stability, C. Han et al., Chem. Eur. J., 17, 445 – 449 (2011); DOI: 10.1002/chem.201001981.
