TIPS-NPh
CAS Number 2499713-87-8
High Purity Sublimed Materials, Materials, OLED Materials, Semiconducting MoleculesTriplet-triplet Annihilation Upconversion (TTA-UC) Naphthalene Derivative
High purity ultraviolet emitter available in sublimed (≥99%) and unsublimed (≥98%) grade
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
TIPS-NPh is a triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion (TTA-UC) ultraviolet emitter featuring high fluorescence quantum yield and high singlet generation efficiency. Known as 1,4-DTNA, TIPS-NPh has a low enough triplet energy level to be sensitized by Ir(C6)2(acac), a superior donor that does not quench UV emission. The combination of TIPS-NPh and Ir(C6)2(acac) realizes efficient UV light production even with weak light sources such as an AM 1.5 solar simulator and indoor LEDs. A visible-to-UV TTA-UC efficiency of over 20% based on TIPS-Nph and Ir(C6)2(acac) is achieved under pulsed excitation at 445 nm. Together with TIPS-NPh, CBDAC—a metal-free ketocoumarin derivative donor which exhibits strong visible absorption, weak UV absorption, and high ISC efficiency—also demonstrates visible-to-UV TTA-UC efficiency of 20.3% under the laser excitation at 445 nm.
TIPS-NPh can also pair with metal-free multiple resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescence (MR-TADF) materials to gain the visible-to-ultraviolet upconversion effect. A high upconversion quantum efficiency of 12.5% is achieved by mixing BNCzBr and TIPS-NPh under laser excitation, owing to the internal heavy atom effect which leads to a significantly decreased PLQY and a remarkably increased intersystem crossing quantum yield.
Its isomer 1,5-DTNA is also available in high purity sublimed and unsublimed grade.
General Information
| CAS Number | 2499713-87-8 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C32H48Si2 |
| Molecular Weight | 488.89 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 333 nm (in toluene) |
| Fluorescence | λem 588 nm (in toluene) |
| Triplet Energy |
ET1 = - 2.12 eV [1] |
| Synonyms | 1,4-DTNA, N-2TIPS, 1,4-Bis((triisopropylsilyl)ethynyl)naphthalene |
| Classification or Family | Naphthalene derivatives, Ultraviolet emitter, Triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion (TTA-UC) |
Product Details
| Purity | Sublimed (≥99%) and unsublimed (≥98%) |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | N/A |
| Appearance | White powder/crystals |
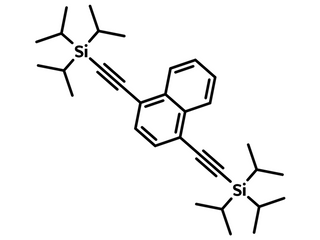
Chemical Structure
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- N. Harada et al. (2020); Discovery of Key TIPS-Naphthalene for Efficient Visible-to-UV Photon Upconversion under Sunlight and Room Light, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 60 (1), 142-147; DOI: 10.1002/anie.202012419.
- M. Uji et al. (2022); Heavy metal-free visible-to-UV photon upconversion with over 20% efficiency sensitized by a ketocoumarin derivative, J. Mater. Chem. C, 10, 4558-4562; DOI: 10.1039/D1TC05526G.
- Y. Shi et al. (2024); Harnessing Heavy-Atom Effects in Multiple Resonance Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence (MR-TADF) Sensitizers: Unlocking High-Performance Visible-to-Ultraviolet (Vis-to-UV) Triplet Fusion Upconversion, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 15 (17), 4647–4654; DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00542.
- A. Olesund et al. (2023); Bulky Substituents Promote Triplet–Triplet Annihilation Over Triplet Excimer Formation in Naphthalene Derivatives, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 145 (40), 22168–22175; DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c08115.
