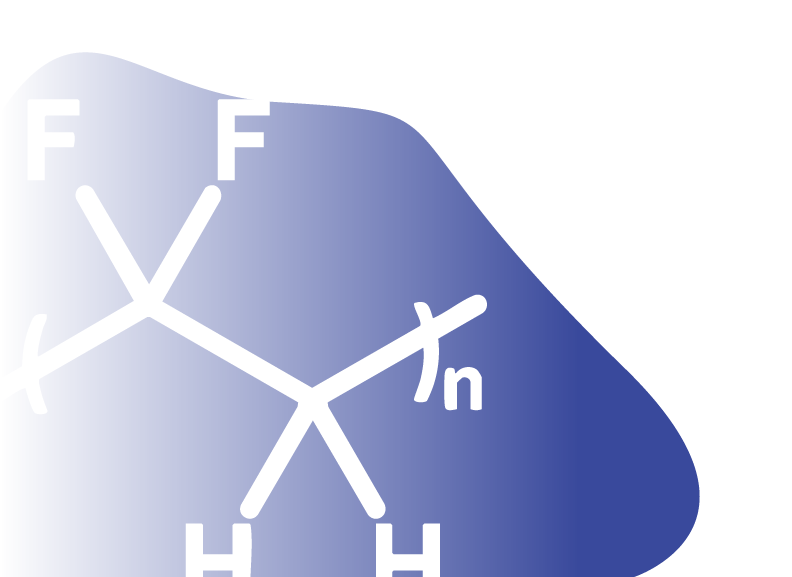
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
CAS Number 24937-79-9
Battery Binders, Battery Materials, Materials, Sodium-Ion Battery MaterialsElectrochemical and thermal stable Polyvinylidene fluoride
used in battery fabrication as a binder, separator and polymer electrolyte
Overview | Product Information | Related Products | Technical Support
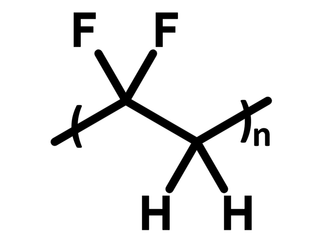
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF, CAS number 24937-79-9) is a chemically inert, thermoplastic polymer. PVDF is a fluorinated polymer with an equivalent amount of CF2 and CH2 groups in the polymer backbone. The CF2 units contribute to its electrochemical and thermal stability. Additionally, the dipole moment between CF2 and CH2 units makes PVDF a polar polymer, resulting in strong piezoelectricities.
PVDF has demonstrated versatile uses across a wide range of applications, with its most notable use in the battery industry. Polyvinylidene fluoride is commonly employed as a binder material in the preparation of composite electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. As a binder, PVDF exhibits good adhesion strength due to its intermolecular hydrogen bonding. It is often combined with conductive additives such as carbon black, graphene oxide, or carbon nanotubes to enhance thermal and electrical conductivity within the electrode.
To further improve the performance of PVDF in lithium-sulfur batteries, the polymer can be modified by grafting polyacrylic acids. The graft polymer can be synthesized by dehydrofluorination of PVDF to generate alkene reaction sites, followed by free radical polymerization with acrylic acid. The resulting Li-S battery cell using PVDF-graft-PAA as the cathode binder exhibits a high reversible capacity of 644.1 mAh/g after 100 cycles.
PVDF also finds its applications in polymer electrolytes and separators. A polymer electrolyte composed of PVDF, cellulose acetate, and aluminum hydroxide displays displays ionic conductivity of 2.85 × 10-3 S/cm (battery capacity of 151.9 mAh/g at 1C). A separator made from PVDF and Al2O3 composite has a porosity of 55.8% and an ionic conductivity of 2.23 × 10-3 S/cm.
Versatile polymer
used as electrode binder, separator and electrolyte
Fluorinated polymer
Electrochemically and thermally stable
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Low volatile content
0.03 %
General Information
| CAS Number | 24937-79-9 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | (C2H2F2)n |
| Full Name | Poly(1,1-difluoroethylene) |
| Molecular Weight | 700k Da |
| Melting Point | 170.1 °C |
| Synonyms | PVDF, poly(vinylene fluoride), polyvinylidene difluoride, PVdF |
| Classification or Family | Battery binder material, fluorinated binder, lithium ion batteries, sodium ion batteries, solid state batteries, polymer composite electrolytes |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Average Particle Size | 104 µm |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melt Flow Index (MFI) | 1.0 g/10 min at 230 °C 21.6 kg (ASTM D1238) |
MSDS Documentation
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) MSDS Sheet
References
- Design of PVDF-g-PAA binder endowing high sulfur loading with enhanced performance of lithium-sulfur batteries, S.-Y. Nam et al., Int. J. Energy Res., 3375897 (2025); DOI: 10.1155/er/3375897.
- Polymeric binders used in lithium ion batteries: actualities, strategies and trends, B. Chen et al., ChemElectroChem, 11, e202300651 (2024); DOi: 10.1002/celc.202300651.
- A comprehensive review of current and emerging binder technologies for energy storage applications, S. Sudhakaran et al., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 6(23), 11773–11794 (2023); DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c02218.
Related Products
We stock a wide range of Battery materials available to purchase online. Please contact us if you cannot find what you are looking for.