DPVBi
CAS Number 142289-08-5
Charge Transport Layer Materials, Fluorescent Host Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Hole Injection Layer Materials,DPVBi, a blue host-emitting material in OLEDs
Enhances hole-injection, current and luminance efficiencies of OLEDs, 4,4 -bis(2,2 -diphenylvinyl)-1,1 -diphenyl, CAS No. 142289-08-5, Sublimed ≥99.0%
DPVBi is a wide band gap small molecule semiconducting material, commonly used as a blue host-emitting material in OLEDs.
It has been reported that DPVBi can effectively manipulate the Schottky energy barrier between the ITO and the emitting layer, and thus significantly enhance hole-injection, current and luminance efficiencies of OLEDs, as well as their stability [1].
General Information
| CAS number | 142289-08-5 |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C40H30 |
| Molecular weight | 510.67 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 351 nm (THF) |
| Fluorescence | λem 447 nm (THF) |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.9 eV, LUMO = 2.8 eV |
| Synonyms |
|
| Classification / Family | Hole-injection materials, Hole-transporting materials, Blue light-emitting materials, Host materials, Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), Organic electronics |
* Measurable with an optical spectrometer
Product Details
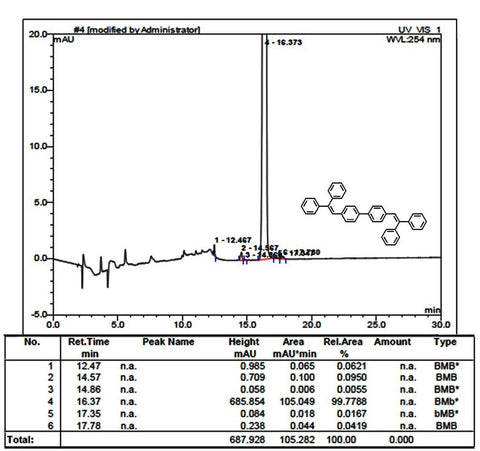
| Purity | Sublimed* >99.0% (HPLC) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 207 °C (lit.) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder/crystals |
* Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals, see sublimed materials.
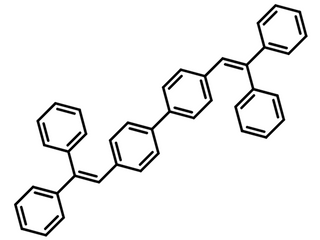
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/CuPc/NPB/DPVBi:DCJTB/Alq/LiF/Al [2] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Luminance | 7,822 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 2.45 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 1.75 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO/ NPB (70 nm)/DPVBi:BCzVBi (15 wt%, 15 nm)/ADN:BCzVBi (15% wt%, 15 nm)/BPhen (30 nm)/ Liq (2 nm)/Al (100 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Color | Deep Blue |
| Max. Luminance | 8,668 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 5.16 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3 (5 nm)/ NPB (35 nm)/CBP (5 nm)/DPVBi (I) (10 nm)/CBP:Rubrene (4:1) (3 nm)/DPVBi (II) (30 nm)/CBP (HBL3) (2 nm)/BPhen (10 nm)/LiF/Al [4] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Luminance | 2,650 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 4.6 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO/NPB/DPVBi:BCzVBi-6%/MADN:DCM2-0.5%/Bphen/Liq/Al [6] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Luminance | 15,400 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 6.19 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO/TBADN:3 wt% DSA-Ph (27 nm)/DPVBi:5 wt% BCzVB (3 nm)/LiF/Al [7] |
|---|---|
| Color | Blue |
| Max. Luminance | 16,530 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 9.77 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 5.68 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | glass/Ag (100 nm)/ITO (90 nm)/2-TNATA (60 nm)/NPB (15 nm)/ DPVBi:DCJTB (1.2%, 30 nm)/Alq3 (20 nm)/Li (1.0 nm)/Al (2.0 nm)/Ag (20 nm)/ITO(63 nm)/SiO2 (42 nm) [8] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Luminance | 14,500 cd/m2 |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 1.4 lm W−1 |
Characterization
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Enhanced Performance of Organic Light Emitting Device by Incorporating 4,4-Bis(2,2-diphenylvinyl)-1,1-Biphenyl as an Efficient Hole-Injection Nano-Layer, W. Yun et al., J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 13 (3), 2166-2170 (2013).
- A white OLED based on DPVBi blue light emitting host and DCJTB red dopant, X. Zheng et al., Display, 24 (3), 121-124 (2003), doi:10.1016/j.displa.2003.09.004.
- Highly efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes using dual emissive layers with host-dopant system, B. Lee et al., J. Photon. Energy. 3(1), 033598 (2013), doi:10.1117/1.JPE.3.033598.
