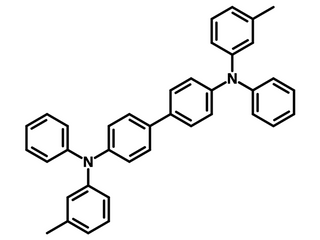
TPD - N,N′-Bis(3-methylphenyl)-N,N′-diphenylbenzidine
CAS Number 65181-78-4
Charge Transport Layer Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Hole Injection Layer Materials, Hole Transport Layer Materials, Host Materials, Materials,TPD, HTL material in organic electronic devices
Used as a blue-violet light emitting material or host material on the PhOLEDs
Overview | Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
N,N′-Bis(3-methylphenyl)-N,N′-diphenylbenzidine, CAS number 65181-78-4, commonly abbreviated as TPD, is widely used as hole transport materials in organic electronic devices.
TPD is also used as a blue-violet light emitting material or host material on the phosphorescence organic light emitting diodes for its wide energy band being about 3.2 eV with highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) being 5.5 eV and 2.3 eV respectively [1, 2].
TPD from Ossila was used in the high-impact paper (IF 14.92), Complete polarization of electronic spins in OLEDs, T. Scharff et al., Nat. Commun., 12, 2071 (2021); DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22191-3.
General Information
| CAS Number | 65181-78-4 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C38H32N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 516.67 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 352 nm in THF |
| Fluorescence | λem 398 nm in THF |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.5 eV, LUMO = 2.3 eV |
| Synonyms | TPD, N,N′-Bis(3-methylphenyl)-N,N′-diphenylbenzidine, N,N'-Diphenyl-N,N'-di(m-tolyl)benzidine, 4,4'-Bis[N-phenyl-N-(m-tolyl)amino]biphenyl |
| Classification / Family | Triphenylamine derivatives, Hole-injection materials, Hole transporting materials, Phosphorescent host materials, Light-emitting diodes, Organic electronics, Sublimed materials |
* Measurable with an optical spectrometer
Product Details
| Purity | Sublimed* >99% |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 175 – 177 °C (lit.) |
| Color | White powder/crystals |
* Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals, see sublimed materials.
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device Structure | ITO/m-MTDATA/TPD/F-TBB*/Alq3/MgAg [1] |
|---|---|
| Color | Blue |
| Max EQE | 1.4% |
| Maximum luminance | 3960 cd m-2 at 15.0 V |
| Device Structure | ITO/75 wt% TPD:25 wt% PC (50nm) /TCTA (10nm)/6 % PtL30Cl*:94 % [TCTA: TCP] [1:1] (30 nm)/TAZ (30 nm)/LiF/Al [3] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| EQE@500 cd/m2 | 11.3% |
| Current Efficiency@500 cd/m2 | 23.5 cd/A |
| Bias | 9.3 V |
| Device Structure | ITO/m-MTDATA*:F4-TCNQ (100 nm)/TPD (5 nm)/Alq3 (20 nm)/BPhen (10 nm)/Bphen:Li (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [4] |
|---|---|
| Color | Green |
| Max. Luminance | 10,000 cd/m2 at 5.2 V |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 5.27 cd/A |
| Device Structure | ITO/CuPc(10 nm)/TPD(50 nm)/Bepp2 (40 nm)/LiF(1.5 nm)/Al(200 nm) [5] |
|---|---|
| Color | Blue |
| Max. Luminance | 4,000 cd/m2 |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 0.55 lm W−1 |
| Device Structure | ITO/TPD (50 nm)/BePP2 (5 nm)/TPD (4 nm)/BePP2:rubrene (5 nm)/TPD (4 nm)/Alq (10 nm)/Al [6] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. Luminance | 20,000 cd/m2 |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 1.11 lm W−1 |
| Device Structure | ITO/CuPc (18 nm)/TPD (50 nm)/Alq3 (60 nm)/BCP (10 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [8] |
|---|---|
| Color | Green |
| Max. Luminance | 5,993 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 3.82 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 2.61 lm W-1 |
| Device Structure | ITO/PEDOT:PSS/PVK:OXD-7:TPD:(Et-Cvz-PhQ)2Ir(pic)*/OXD-7 (20 nm)/Ba (3 nm)/Al (100 nm) [9] |
|---|---|
| Color | Red |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 17.5 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 10.6% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 6.42 lm W−1 |
| Device Structure | ITO/TPD (50 nm)/Zn(BTZ)2 (50 nm)/MgIn (200 nm) [10] |
|---|---|
| Color | Greenish-White |
| Max. Luminance | 10,190 cd/m2 |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 0.89 lm W−1 |
*For chemical structure informations please refer to the cited references.
Characterization

MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Development of high-performance blue-violet-emitting organic electroluminescent devices, K. Okumoto et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 79(9), 1231–1233 (2001).
- Efficiency and Aging Comparison Between N,N′-Bis (3-methylphenyl)-N,N′-diphenylbenzidine (TPD) and N,N′-Di-[(1-naphthalenyl)-N,N′-diphenyl]-1,1′-biphenyl-4,4′-diamine (NPD) Based OLED Devices, M. Maglione et al., Macromol. Symp., 247, 311–317 (2007).
- Blue-shifting the monomer and excimer phosphorescence of tridentate cyclometallated platinum(II) complexes for optimal white-light OLEDs, L. Murphy et al., Chem. Commun., 48, 5817-5819 (2012), DOI: 10.1039/C2CC31330H.