Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) Crystal
CAS Number 1317-33-5
2D Materials, Low Dimensional Materials, Materials, Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2), Transition Metal Chalcogenides (TMCs), Transition Metal Dichalcogenides (TMDs)Molybdenum disulfide crystal, one of the most studied and celebrated TMDCs
Highly anisotropic with excellent nonlinear optical properties
Technical Data | MSDS | Structure | Literature and Reviews | Related Products | Resources and Support
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), CAS number 1317-33-5, is a member of the transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) family. Due to its natural availability as molybdenite, it is one of the most studied and celebrated TMDCs.
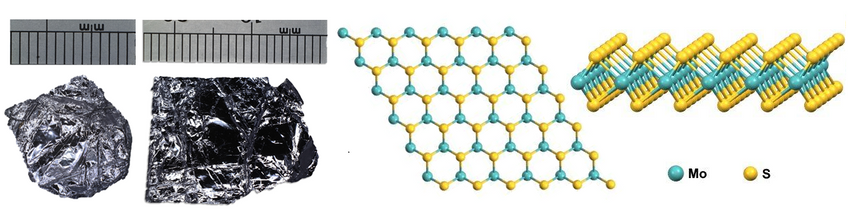
Like graphene, MoS2 has a similar two-dimensional layered structure, with each individual layer stacked upon each other to form the bulk single crystal. Each layer of MoS2 is composed of a plane of hexagonally-arranged molybdenum atoms, positioned between two planes of hexagonally-arranged sulfur atoms. Like graphite, each layer is bound by weak van der Waals forces. Because of this, it is possible to obtain monolayer to few-layer crystal flakes from a bulk crystal via mechanical exfoliation (using scotch tape).
High Purity
High purity ≥99.999% MoS2 Crystal
Worldwide Shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Low Cost
Low Cost Molybdenum Disulfide
Wide Range of Applications
Applications in electronic and optoelectronic devices
MoS2 has an indirect band-gap of 1.23 eV for bulk single crystal or multi-layer films. However, single atomic layers have a direct band-gap of 1.9 eV. Due to its layered structure, MoS2 is highly anisotropic with excellent nonlinear optical properties. It is widely used as a high-performance lubricant.
As a result of its direct band-gap, single-layer MoS2 has received much interest for applications in electronic and optoelectronic devices (such as transistors, photodetectors, photovoltaics and light-emitting diodes). It is also being explored for applications in photonics, and can be combined with other TMDCs to create advanced heterostructured devices.
Molybdenum disulfide is manufactured via chemical vapor transport (CVT) crystallization, with purities of over 99.999% achieved. It can used to create monolayer and few-layer MoS2 by mechanical or liquid exfoliation. Single crystals can also be studied using a range of microscopies (including AFM and TEM).
Technical Data
| CAS Number | 1317-33-5 |
| Chemical Formula | MoS2 |
| Molecular Weight | 160.07 g/mol |
| Bandgap | 1.23 eV [1] |
| Preparation | Synthetic - Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) |
| Structure | Hexagonal |
| Electronic Properties | 2D semiconductor |
| Melting Point | 2375 °C (lit.) |
| Color | Black / Dark brown |
| Synonyms | Molybdenum sulfide, Molybdenum disulfide, Molybdenum(IV) sulfide |
| Classification / Family | Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), 2D semiconductor materials, Nano-electronics, Nano-photonics, Materials science |
Product Details
| Form | Purity |
|---|---|
| Crystal | ≥99.999% |
Pricing Table
| Product Code | Form | Size* | Quantity (EA) | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2107A10 | Crystal | Small (10 × 10 mm2) | 1 | £460 |
| M2107A15 | Crystal | Medium (15 × 15 mm2) | 1 | £850 |
| M2107A20 | Crystal | Large** (20 × 20 mm2) | 1 | £1150 |
* Typical representative size, areas/dimensions may vary
** Item with a lead time of 2 - 3 weeks, please contact for more information
MSDS Document
Molybdenum Disulfide Structure
Literature and References
- Few-Layer MoS2: A Promising Layered Semiconductor, R. Ganatra et al., ACS Nano, 8 (5), 4074–4099 (2014); DOI: 10.1021/nn405938z.
- Atomically Thin MoS2: A New Direct-Gap Semiconductor, K. Mak et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 136805 (2015); DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.136805.
- Shape-Uniform, High-Quality Monolayered MoS2 Crystals for Gate-Tunable Photoluminescence, X. Zhang et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 9, 42121−42130 (2017); DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b14189.
Related Products
We stock a wide range of 2D materials available to purchase online. Please contact us if you cannot find what you are looking for.



