BAlq
BAlq, photochemically stable blue-emitting layer material in OLEDs
Used to improve the efficiency and lifetime of PHOLEDs, Sublimed ≥99%, CAS No. 146162-54-1
Bis(8-hydroxy-2-methylquinoline)-(4-phenylphenoxy)aluminum, known as BAlq or BAlq3, is widely used as blue-emitting layer materials in organic light-emitting diodes. It is also used as hole-blocking layer or as a “barrier-softening” interfacial layer in between the electron transporting and emissive layers [1, 2, 3, 4].
BAlq is also applied as the host material and electron-transport type hole-blocking layer in red PHOLEDs, and to improve the efficiency and lifetime of PHOLEDs. As a hole-blocking material, it is known to allow for high lifetimes, up to 160,000 hours at a luminance level of 100 cd/m2 [3].
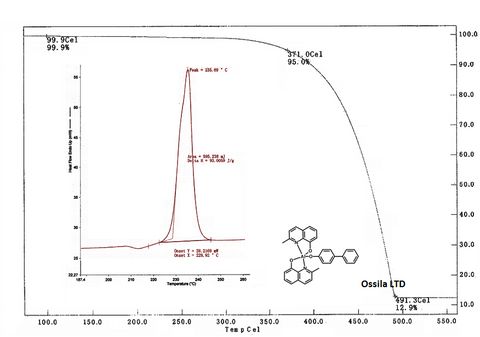
BAlq has a glass transition temperature of 99 °C and is photochemically stable [5].
General Information
| CAS number | 146162-54-1 |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C32H25AlN2O3 |
| Molecular weight | 512.53 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 259 nm (in THF) |
| Fluorescence | λem 334,477 nm (in THF) |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.9 eV, LUMO = 2.9 eV |
| Synonyms |
|
| Classification / Family |
Electron transporting materials, Hole blocking materials, Light emitter layer materials, Phosphorescent host materials, Organic light-emitting diodes, Organic electronics, Sublimed materials |
Product Details
| Purity | ≥99% (sublimed) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | Melting point/range: 207 - 214 °C (lit.) |
| Color | Light-yellow powder/crystals |
*Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals. For more details about sublimation, please refer to the Sublimed Materials.
Chemical Structure

Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO (110 nm)/NPB(80 nm)/BtpIr*-doped BAlq (47.5 nm)/Alq3(30 nm)/Li2O(0.5nm)/Al(100nm) [5] |
|---|---|
| Color |
|
| Max. EQE | 8.6% |
| Max. Luminance | 179 cd/m2 |
| Device structure | ITO/CuPc (15 nm)/NPB (80 nm)/NPB: 0.5 wt% DCJTB (20 nm) /Alq3:0.5 wt% C545T (3 nm)/MADN:0.8 wt% DSA-ph*(40 nm)/BAlq3 (10 nm)/LiF/Al [6] |
|---|---|
| Color |
|
| Max. Luminance | 45,000 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 20.8 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 15.9 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO/MoOx (5 nm)/NPB (40 nm)/4% Y-Pt*:TCTA (20 nm)/8% FIrpic:mCP(10 nm)/8% FIrpic:UGH2 (10 nm)/BAlq (40 nm)/LiF (0.5 nm)/Al (100 nm) [7] |
|---|---|
| Color |
|
| Max. EQE | 16.0% |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 45.6 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 35.8 lm W−1 |
*For chemical structure informations please refer to the cited references
Characterization (TGA and DSC)
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Electroluminescent properties of organic light-emitting diodes using BAlq and Alq3 co-evaporation layer, Y. Iwama et al., Thin Solid Films 499, 364-368 (2006).
- Electroluminescent mechanism of organic light-emitting diodes with blue-emitting Alq, T. Itoh et al., Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 284–285, 594–598 (2006).
- A host material containing tetraphenylsilane for phosphorescent OLEDs with high efficiency and operational stability, J-W. Kang et al., Org. Electronic, 9, 452–460 (2008).
