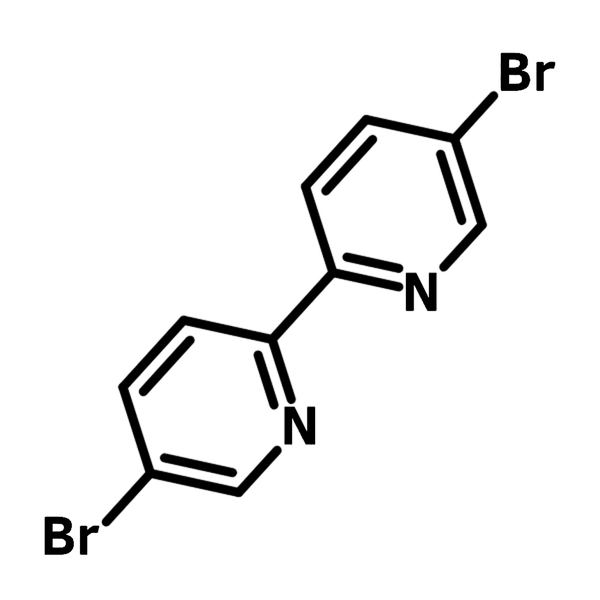
5,5'-Dibromo-2,2'-bipyridine
CAS Number 15862-18-7
Chemistry Building Blocks, Dibromo Monomers, Heterocyclic Building Blocks, Materials,A well-known bipyridine ligand with two bromo-functional groups
A bidentate ligand for organometallic compound in application of OLEDs, DSSCs and photosensitizers
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
5,5'-Dibromo-2,2'-bipyridine (CAS number 15862-18-7), derived from bipyridine, is a bromine functionalized building block with popular use as a chelating ligand for ruthenium (Ru) or iridium (Ir) organometallic complexes. Bipyridine-Ru complexes exhibit excellent photoluminescence and electrochemiluminescence for OLEDs and DSSCs, owing to the strong intraligand (π-π*) and metal-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) transition bands.
Bearing dibromo function groups, 5,5'-Dibromo-2,2'-bipyridine allows further functionalization to form larger conjugated molecules. Bipyridine derivatives can react with borane species to form organoboron compounds as electron acceptor in organic photovoltaics. By extending the chromophore size of the bipyridine core, these types of ligands are employed as photosensors for the detection of fluoride ions. This linear building block is also ideal for bridging different functional molecules for modifying energy band gap and intramolecular spacing.
Bipyridine building block
for the synthesis of OLED and organic photovoltaic materials
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Capped with bromides
for facile coupling reactions
High purity
>98% Purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 15862-18-7 |
| Chemical Formula | C10H6Br2N2 |
| Full Name | 5,5'-Dibromo-2,2'-bipyridine |
| Molecular Weight | 313.98 g/mol |
| Synonyms | 5-bromo-2-(5-bromopyridin-2-yl)pyridine |
| Classification / Family | Bipyridine derivatives, Heterocyclic building blocks, Dyes, Semiconductor synthesis intermediates, OLED, OFETs, organic photovoltaics |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Purity | >98% (1H NMR) |
| Melting Point | Tm = 226 - 227 °C |
| Appearance | Off-white powder |
MSDS Documentation
5,5'-Dibromo-2,2'-bipyridine MSDS Sheet
Literature and Reviews
-
Synthesis, photoluminescence and electrochemiluminescence of ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes based on bipyridine derivatives with carbazole moieties, H. -Y. Li et al., Inorg. Chim. Acta., 370, 398-404(2011); DOI: 10.1016/j.ica.2011.02.012.
-
Heteroleptic ruthenium complexes containing uncommon 5,5'-disubstituted-2,2'-bipyridine chromophores for dye-sensitized solar cells, F.-R. Dai et al., Dalton Trans., 40, 2314–2323(2011); DOI: 10.1039/c0dt01043j.
-
Oligomeric ligands incorporating multiple 5,5'-diethynyl-2,2'-bipyridine moieties bridged and end-called by 3,4-dibutylthiophene units, S. Goeb et al., J. Org. Chem., 70, 1518-1529(2005); DOI: 10.1021/jo048435i.
