FBR molecule, NFA which reduces the tendency of crystallization
Used to achieve one of the highest open voltages for polymer organic solar cells
Specifications | Pricing and Options | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
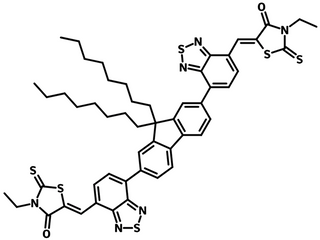
FBR (CAS number 1644381-95-2) having a similar AA-D-AA type structure to IDFBR, contains electron-donating alkylated fluorene as the core, flanked by electron withdrawing benzothiadiazole (BT) and 3-ethylrhodanine units on the periphery terminals.
FBR reduces the tendency of crystallization and helps to prevent the formation of large crystalline domains in the BHJ donor/acceptor blend composition leading to better device performance efficiency and longer life-times.
Comparing to PC71BM, FBR has a relatively high lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) which in theory should give a higher open voltage (Voc). This is indeed the case for polymer organic solar cells with PffBT4T-2DT as the polymer donor and FBR as the electron acceptor, yielding a device performance efficiency over 7.8% with an open voltage of 1.12 eV. This is one of the highest achieved open voltages for polymer organic solar cells.
Device structure: ITO/ZnO/PffBT4T-2DT:FBR/MoOx/Ag [1]
| Thickness (nm) | VOC (V) | JSC (mA cm-2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
| 120 | 1.12 | 11.5 | 61 | 7.8 |
General Information
| CAS Number | 1644381-95-2 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C53H56N6O2S6 |
| Purity | >98% (1H NMR) |
| Full Name | 5,5′-[(9,9-Dioctyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)bis(2,1,3-benzothiadiazole-7,4-diylmethylidyne)]bis[3-ethyl-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone] |
| Molecular Weight | 1001.44 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 510 nm (Film) |
| HOMO / LUMO | HOMO = -5.83 eV, LUMO = -3.75 eV [1] |
| Solubility | Chloroform, chlorobenzene |
| Form | Red powder/crystals |
| Synonyms | (5Z,5'Z)-5,5'-((7,7'-(9,9-dioctyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)bis(benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-7,4-diyl))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-ethyl-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one) |
| Classification / Family | NFAs, n-type non-fullerene electron acceptors, Organic semiconducting materials, Low band-gap small molecule, Small molecular acceptor, Organic photovoltaics, Polymer solar cells, NF-PSCs. |
* Measurable with an optical spectrometer
Chemical Structure
Pricing
| Batch | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|
| M2242A1 | 100 mg | £265 |
| M2242A1 | 250 mg | £530 |
| M2242A1 | 500 mg | £800 |
| M2242A1 | 1 g | £1360 |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Reduced voltage losses yield 10% efficient fullerene free organic solar cells with >1 V open circuit voltages, D. Baran et al., Energy Environ. Sci., 9, 3783--3793 (2016); DOI: 10.1039/c6ee02598f.
- A Rhodanine Flanked Nonfullerene Acceptor for Solution-Processed Organic Photovoltaics, S. Holliday et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 137, 2, 898–904 (2015); doi: 10.1021/ja5110602.
- Critical review of the molecular design progress in non-fullerene electron acceptors towards commercially viable organic solar cells, A. Wadsworth et al., Chem. Soc. Rev., 48, 1596 (2019); DOI: 10.1039/c7cs00892a.
Related Products
Semiconducting polymers for bulk heterojunction, OPV, OLED, OFET and perovskite interfaces and solar cell research.


