DTT, Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene
CAS Number 3593-75-7
Chemistry Building Blocks, Heterocyclic Building Blocks, Materials, Monomers,High-purity, low price DTT for chemical synthesis
Building block for semiconducting small molecules, oligomers, and polymers
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
Having three fused thiophene units, DTT (or Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene), CAS number 3593-75-7, is a chemical which is widely used as building block for the synthesis of semiconducting small molecules, oligomers, and polymers. Fused DTT offers a highly conjugated backbone structure for its rigid and flat molecular structure and extended π-conjugation. This affords compact molecular packing in thin films and results in enhanced electrical performance.
Apart from the π-π interactions which originate from the close molecular packing, intermolecular S-S interactions also play an important role for solid film morphology, with enhanced charge transport within the effective dimensionality of the electronic domains. DTT derivatives exhibit large bandgap energy due to their high resonance stabilization energy, regardless of their rigid and flat backbone structures and compact molecular packing in thin films. When they have larger energy band gaps (>2.09 eV) and lower HOMO levels (< −5.02 eV) than pentacene, compounds including DTT derivatives are generally treated as the ambient stable materials.
α-Dimeric DTT (biDTT) has been used in OFETs as an active layer material, and showed interesting device characteristics, with a relatively high charge mobility of 0.05 cm2 V–1 s–1 and large on/off ratios of ~108. Low bandgap semiconducting copolymer PDTTDPP, which alternates dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene and diketopyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrolediketopyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrolediketopyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrolediketopyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole (DPP), shows great OFET device performance. PDTTDPP has a hole mobility of 0.60 cm2 V−1 s−1 without post-treatment and a promising power conversion efficiency of 6.05% in organic photovoltaics with PC71BM as an electron acceptor.
2,6-Dibromodithieno[3,2-b:2',3'-d]thiophene can be prepared by brominating dithieno[3,2-b:2',3'-d]thiophene with N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) in acetic acid at room temperature. Direct arylation of 2,6-Dibromodithieno[3,2-b:2',3'-d]thiophene can afford DTT-8, which self-organizes into single-crystal microribbons or microsheets via solution processing. High carrier mobilities of up to 10.2 cm2 V−1 s−1 and high on/off ratios of ∼107 have been achieved in organic single-crystal field-effect transistors.
The highly crystalline nature of DTT can also restrict the over self-assembling of the A-DA′D-A acceptors during the film casting process, which allows the refining of phase separation and molecular packing with the volatilization of DTT under thermal annealing (TA) treatment. PTQ10:m-BTP-PhC6:PC71BM-based ternary OSCs processed by the dual additives of 1-chloronaphthalene (CN) and DTT record an outstanding power-conversion efficiency of 18.89%, with a remarkable fill factor (FF) of 80.6%.
Organic materials made of DTTs display interesting properties in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and organic solar cells (OSC) devices. DTT based semiconductors exhibit high crystallinity, charge carrier mobility and excellent environmental and thermal stabilities.
Dithienothiophene building block
for the synthesis of OLED and organic photovoltaic materials
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Planar and rigid
Promoting self-assemble layered structure
High purity
>98% Purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 3593-75-7 |
| Chemical Formula | C8H4S3 |
| Full Name | Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene |
| Molecular Weight | 196.31 g/mol |
| Synonyms | DTT |
| Classification / Family | Bithiophene, semiconductor synthesis intermediates, low band gap polymers, OLED, OFETs, solid additive (SA), organic photovoltaics |
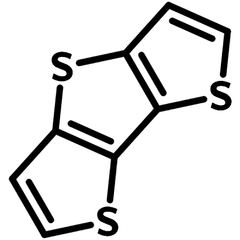
Chemical Structure
Dithieno[3,2-b:2',3'-d]thiophene consists of three annulated thiophene rings with a 2,2’-bithiophene (BT) unit bridged by a sulfur atom to produce a central thiophene ring between the two originals. The central sulfur points in the opposite direction to the two neighbouring atoms. The structure of DTT could be also described as a thieno[3,2-b]thiophene (TT) molecule fused to an additional thiophene.
Product Details
| Purity | >98% (1H NMR in CDCl3) |
| Melting Point | 65 °C - 70 °C |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
MSDS Documentation
Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene (DTT) MSDS Sheet
Literature and Reviews
- Synthesis and fluorescence emission properties of D-π-D monomers based on dithieno[3,2-b:2',3'-d]thiophene, C. Wang et al., J. Lumin., 188, 388-393 (2017); DOI: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.04.060.
- Development of Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene (DTT) Derivatives as Solution-Processable Small Molecular Semiconductors for Organic Thin Film Transistors, E. Choi et al., Coatings, 11(10), 1222 (2021); DOI: 10.3390/coatings11101222.
- Tetraphenylethylene substituted thienothiophene and dithienothiophene derivatives: synthesis, optical properties and OLED applications, R. Isci et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 8, 7908-7915 (2020); DOI: 10.1039/D0TC01715A.
![DTT, Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene CAS 3593-75-7](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/files/dtt-chemical-structure.png?v=1718724963&width=380)