Br-2PACz
CAS Number 2762888-11-7
Charge Transport Layer Materials, Hole Transport Layer Materials, Materials, OLED Materials,Self-assembled Monolayer for Stable Solar Cells
Br-2PACz, Carbazole-based phosphonic acid hole transport or extraction layer for NFA-polymer solar cells and p-i-n perovskite solar cells
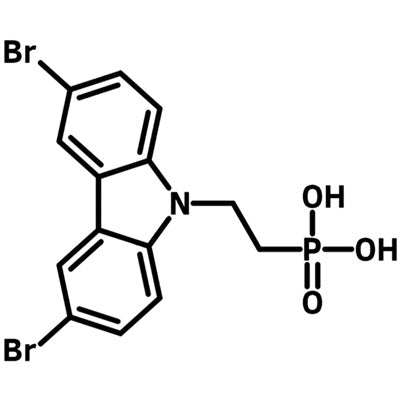
Br-2PACz ((2-(3,6-dibromo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)ethyl)phosphonic acid, CAS No. 2762888-11-7), a dibrominated derivative of 2PACz, is a self-assembled monolayer material. It has an electron-rich carbazole terminal unit and a ethyl phosphonic acid head group.
Carbazole-based self-assembled monolayers have been widely used in Pb-based perovskite solar cells and silicon-perovskite tandem devices. The work function of indium-tin-oxide increases dramatically from 4.73 eV to 5.82 eV upon functionalization with Br-2PACz.
A record efficiency of 19.51% was achieved in Cs0.25FA0.75Sn0.5Pb0.5I3 perovskite solar cells when Br-2PACz was engaged as a hole transport layer material, while an efficiency of 16.33% was recorded by using PEDOT:PSS. The Br-2PACz-based devices also gave better device stability and longer shelf-life, maintaining 80% of their initial efficiency under continuous illumination for 230 h, even after the fabricated device was being stored in a N2 atmosphere for 4224 h [1].
Serving as hole selective contact for organic solar cells and perovskite solar cells, Br-2PACz is an alternative to PEDOT:PSS with superior performance with the convenience of solution deposition at low concentration, i.e. 1 mM.
Solution Processing Procedure
Typical processing solvents: ethanol, methanol, THF, IPA, DMF
Typical concentration: 1 mM (0.433 mg/ml) or 1.0 mg/ml (1 mg Br-2PACz is dissolved in 1 ml ethanol)
Typical processing procedure: 100 uL of Br-2PACz solution is deposited onto the center of the substrate surface and spin-coated for 30 s at the speed of 3000 rpm. After the coated substrate was annealed for 10 min at 100 ℃, EtOH solution (200 µl) was dynamically spin coated on ITO/SAM at 3000 rpm for 30 s to remove the aggregates, and the substrates was then again annealed at 100 °C for 1 min.
General Information
| CAS Number | 2762888-11-7 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C14H12Br2NO3P |
| Molecular Weight | 433.03 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 458 nm (ITO) |
| Fluorescence | λem (n.a.) |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 6.01 eV, LUMO = 2.64 eV |
| Synonyms | (2-(3,6-Dibromo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)ethyl)phosphonic acid |
| Classification or Family | Carbazole derivatives, Self-assembly monolayers, Hole transport layer, Hole extraction layer, p-i-n Perovskite solar cells, Organic photovoltaics |
Product Details
| Purity | > 99% (1H NMR) |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | n.a. |
| Appearance | Off-white powder/crystals |
Chemical Structure
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- 18.4 % Organic Solar Cells Using a High Ionization Energy Self-Assembled Monolayer as Hole-Extraction Interlayer, Y. Lin et al., ChemSusChem, 14 (17), 3569-3578 (2021); DOi: 10.1002/cssc.202100707.
-
A carbazole-based self-assembled monolayer as the hole transport layer for efficient and stable Cs0.25FA0.75Sn0.5Pb0.5I3 solar cells, M. Pitaro et al., J. Mater. Chem. A, 11, 11755-11766 (2023); DOI: 10.1039/D3TA01276J.
-
18.9% Efficient Organic Solar Cells Based on n-Doped Bulk-Heterojunction and Halogen-Substituted Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole Extracting Interlayers, Y. Lin et al., Adv. Energy Mater., 12 (45), 2202503 (2022); DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202202503.
-
18.73% efficient and stable inverted organic photovoltaics featuring a hybrid hole-extraction layer, Y. Lin et al., Mater. Horiz., 10, 1292-1300 (2023); DOI: 10.1039/D2MH01575G.
-
Tuning the Surface Energy of Hole Transport Layers Based on Carbazole Self-Assembled Monolayers for Highly Efficient Sn/Pb Perovskite Solar Cells, M. Pitaro et al., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2306571 (2023); DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202306571.
- High-Efficiency Perovskite–Organic Blend Light-Emitting Diodes Featuring Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole-Injecting Interlayers, M. Gedda et l., Adv. Energy Mater., 13 (33), 2201396 (2023); DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202201396.
Licensed by Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH in Germany and Kaunas University of Technology in Lithuania.
