Applications of a Glove Box

A glove box creates a controlled environment that protects sensitive samples from water and oxygen, improving results and safety in many applications. In some cases, working in an inert atmosphere is essential for the success of your experiment, for example:
- Working with or storing materials that oxidize, hydrolyze, or degrade when exposed to air.
- Working with hygroscopic materials that absorb water (and clump) as soon as they are exposed to ambient conditions.
- Working with pyrophoric chemicals, such as alkali metals, metal hydrides, and alkyl metal hydrides. These chemicals react violently with air or with moisture and must be used under controlled, inert conditions.
- Working with emergent technologies that can suffer degradation under ambient conditions. These can include materials used in 3rd generation photovoltaics or lithium-ion battery technology.
Glove Box

On This Page
- Inert Atmosphere Processing
- Applications
- Chemical Synthesis
- Organic Electronics
- Additive Manufacturing
- Materials Handling and Storage
- Characterization of Air Sensitive Materials
- Photovoltaics and Solar Cell Research
- Battery Technology
- Nanotechnology
- Catalysis and Chemical Engineering
- Environmental Research
- Opting for a Glove Box
- Read More
Inert Atmosphere Processing
Inert is just another word for chemically inactive. An inert atmosphere is a contained environment filled with a gas that does not react with sensitive chemicals. Helium, nitrogen, or argon are generally used to create inert environments as they are very stable elements. Nitrogen is the most common choice for inert processing, as it is the cheapest. However, nitrogen environments can have issues with static which can make powder processing difficult. For some biological applications, H2 and CO2 can also be used to create an inert environment.
Applications
The Ossila Glove Box automatically keeps the internal atmosphere below your set threshold, so it is suitable for use over an extended period of time. The low cost and ease of use allows the system to be set up as a dedicated environment for specific experiments. This reduces the chances of cross contamination with other users of your lab space.
Inert atmosphere processing is useful for a wide range of experiments across several different fields, including materials science, chemistry, biological research, and pharmaceuticals.
Chemical Synthesis
The automated atmosphere control process built into our glove box ensures the utmost safety for both your stored materials and the experiment itself, shielding them from any exposure. The ability to access services such as power, vacuum lines, and cooling feedthroughs via standard connectors enables you to explore a wide variety of synthesis routes.
Organic Electronics
You can use equipment such as a spin coater, with or without a syringe pump, to deposit thin film structures without exposing them to air. With the antechamber, transferring samples to other systems for testing or the processing of other layers is simple. Examples of electronics fabricated in a glove box include organic light emitting diodes, organic lasers, and other semiconductor devices.
Additive Manufacturing
Integrate an inert environment into your 3D printing process. By housing your printer inside the chamber, it is simple to move parts out of the glove box, ready for testing or shipping. In addition, you can leave materials inside the system to avoid exposing them to ambient air. Move new spools or resin containers through the antechamber to keep the internal atmosphere inert.
Materials Handling and Storage
Store materials permanently without risk of exposure to water or oxygen. With the addition of a microbalance, it is also possible to decant small quantities of materials without having to expose it to an ambient atmosphere. You can also use the glove box to seal materials under nitrogen or argon for safe transport.
Characterization of Air Sensitive Materials
With ample space inside the main chamber, you are able to conduct a number of simple characterization and testing experiments. From the Ossila testing range, the solar cell testing kit, the USB spectrometer, and more, you can characterize air sensitive samples and electronics without exposing them to ambient conditions, and without encapsulation.
Battery Technology
Manufacture battery technology in a moisture-free environment. The incorporation of standard feedthroughs allows you to use data and power feedthroughs so that you can interface with equipment to measure your devices. This gives you complete control and the ability to eliminate moisture from your experiment.
Photovoltaics and Solar Cell Research
The fabrication of thin film perovskite devices in an ambient atmosphere often leads to incorrect morphology or incomplete conversion, and results in devices that do not work. By using a glove box, you can optimize parameters in your fabrication routine in a consistent environment. This eliminates the uncertainty of atmospheric conditions and protects air sensitive layers in your device from degradation until they can be suitably encapsulated.
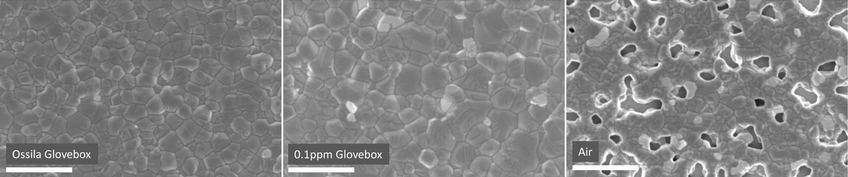
Nanotechnology
Working with or synthesizing nanoparticles, nanowires, and other nanoscale materials can benefit from the use of a glove box. Due to the scale of nanotechnology, these materials are extremely surface dependent, making them all the more vulnerable to contamination. The controlled environment will prevent contamination or oxidation of the samples during synthesis, manipulation, or characterization, enabling you to consistently make high quality materials.
Catalysis and Chemical Engineering
In catalytic reactions, catalysts, reactive intermediates, and other sensitive materials require moisture- and oxygen-free conditions. Set up the hot-plates and glassware needed conduct simple reactions in the main chamber and bring air sensitive materials into the system using the antechamber.
Environmental Research
Often environmental samples, such as metal complexes in soils or water samples, require controlled atmospheres to avoid sample degradation. For this, you can employ glove boxes to handle, store, and study these samples while maintaining their integrity.
Opting for a Glove Box
The Ossila Glove Box is a straightforward and affordable way to create an atmosphere with extremely low levels of H2O and O2. Useful for any process that might be affected by normal atmospheric conditions, particularly chemistry and materials science. Common applications include chemical synthesis, thin film device fabrication, and the handling, preparing, or storing air and moisture sensitive materials.
Choosing to work in the controlled environment of a glove box can guarantee sensitive experiments are successful, while improving the efficiency of your workflow.
Glove Box

Learn More
 Air Sensitive Compounds
Air Sensitive Compounds
There are many reasons that a compound would be sensitive to air. The magnitude of an air-sensitive material's reaction to oxygen or moisture can vary dependent on the material properties.
Read more... Glove Box Pressure: Positive or Negative?
Glove Box Pressure: Positive or Negative?
Glove boxes are essential tools for creating controlled atmospheres where you can handle hazardous or air sensitive materials. They can be maintained at positive pressure or negative pressure.
Read more...