2,6-Dibromoanthraquinone
CAS Number 633-70-5
Chemistry Building Blocks, Dibromo Monomers, Materials, Monomers,A widely used electron deficient anthraquinone building block
For the synthesis of semiconducting small molecules or polymers in application of fluorophores, photocatalyst, OLEDs and organic solar cells
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
2,6-Dibromoanthraquinone (CAS number 633-70-5) has an electron deficient structure of anthracene-9,10-dione with bromo substituents at 2,6-position of the anthraquinone ring. Both the bromo and 9,10-dione functional groups enable the anthracene core to extend its conjugation for the preparation of more complex structures, i.e., semiconducting small molecules or polymers in application of fluorophores, photocatalyst, OLEDs and organic solar cells.
Containing anthraquinone center prepared by cross-coupling reaction between 2,6-dibromoanthraquinone and 1,1,2,2-tetrakis(4-ethynylphenyl)ethene, conjugated organic polymer (AQTEE-COP) demonstrated efficient photocatalytic H2O2 production with an initial rate of 3204 μmol g-1 h-1 under visible light (λ ≥ 400 nm) irradiation without any additional photosensitizers, organic scavengers, or co-catalysts.
Developed for bioimaging in the NIR-II window, novel donor–acceptor–donor type second near-infrared AIE fluorophores AQMN, based on strong electron-acceptor 2,2′-(anthracene-9,10-diylidene) dimalononitrile which was also derived from 2,6-dibromoanthraquinone, exhibit good photostability and can be used in mouse ear vessel imaging with high resolution (FWHM = 93.4 μm/SBR = 1.5) after capsuling in nanoparticles with good biocompatibility.
Anthraquinone building block
for the synthesis of OLED and organic photovoltaic materials
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Capped with bromides
for facile coupling reactions
High purity
>96% Purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 633-70-5 |
| Chemical Formula | C14H6Br2O2 |
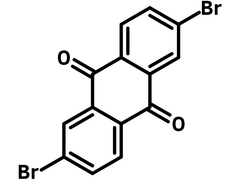
| Full Name | 2,6-Dibromoanthraquinone |
| Molecular Weight | 366.01 g/mol |
| Synonyms | 2,6-DBAQ, 2,6-Dibromoxyanthracene-9,10-dione |
| Classification / Family | Anthraquinone derivatives, Dyes, Semiconductor synthesis intermediates, OLED, OFETs, organic photovoltaics |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Purity | >96% (1H NMR) |
| Melting Point | Tm = 290 °C (lit.) |
| Appearance | Yellow/brown powder |
MSDS Documentation
2,6-Dibromoanthraquinone MSDS Sheet
Literature and Reviews
-
Aggregation-induced emission fluorophores based on strong electron-acceptor 2,2′-(anthracene-9,10-diylidene) dimalononitrile for biological imaging in the NIR-II window, Z. Yang et al., Chem. Commun., 57, 3099-3102 (2021); DOI: 10.1039/D1CC00742D.
-
New Anthraquinone-Based Conjugated Microporous Polymer Cathode with Ultrahigh Specific Surface Area for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries, A. Molina et al., Adv. Funct. Mater., 30 (6), 1908074 (2020); DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201908074.
-
Anthraquinone-Enriched Conjugated Microporous Polymers as Organic Cathode Materials for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries, M. Moharmed et al., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 4 (12), 14628–14639 (2021); DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.1c03270.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of a New Series of Blue Fluorescent 2,6-Linked 9,10-Diphenylanthrylenephenylene Copolymers and Their Application for Polymer Light-Emitting Diodes, H. Chen et al., Macromolecules, 43 (8), 3613–3623 (2010); DOI: 10.1021/ma100195m.
-
Triphenylamine–anthraquinone based donor–acceptor conjugated microporous polymers for photocatalytic hydroxylation of phenylboronic acids, S. Sau et al., Chem. Commun., 59, 635-638 (2023); DOI: 10.1039/D2CC05334A.
-
Highly Crystalline 2,6,9,10-Tetrakis((4-hexylphenyl)ethynyl)anthracene for Efficient Solution-Processed Field-effect Transistors, J. Hur et al., Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 33 (5), 1653-1658 (2012); DOI: 10.5012/bkcs.2012.33.5.1653.
-
Synthesis and Characterizations of Poly(9,10-bisarylethynyl-2,6-anthrylene)s and Poly(9,10-bisalkynyl-2,6-anthrylene), W Cui et al., Macromolecules, 42 (21), 8021–8027 (2009); DOI: 10.1021/ma901514q.
- Conjugated Organic Polymers with Anthraquinone Redox Centers for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Peroxide Production from Water and Oxygen under Visible Light Irradiation without Any Additives, X. Xu et al., ACS Catal., 12 (20), 12954–12963 (2022); DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.2c04085.
