6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo
CAS Number 1147124-21-7
Chemistry Building Blocks, Heterocyclic Building Blocks, Materials, MonomersHigh-Quality 6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo
A naturally occurring isomer of indigo to develop a large number of molecular and polymeric materials for organic electronics with exceptional optical and electrical properties.
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
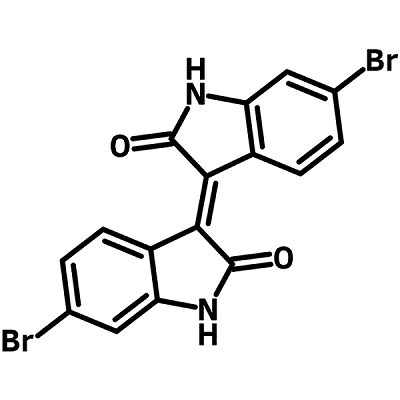
6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo (CAS number 1147124-21-7) contains two identical fused benzolactam rings that are joined by a double bond as a trans isomer, (E)-6,6'-Dibromo-[3,3'-biindolinylidene]-2,2'-dione. Isoindigo is a naturally occurring isomer of indigo which is one of the oldest known dyes found in the leaves of Isatis tinctoria.
6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo is strongly electron deficient character with multiple functional groups and it has proven successful as an electron-accepting component for the preparation of electroactive materials for organic electronics. The N-H functional groups provide opportunity for adding alkyl chain to improve solubility and the Br groups enable to extend the conjugation to the core structure. The high yielding and scalable synthesis have made it possible for rapid development of a large number of isoindigo based molecular and polymeric materials with remarkable physical properties.
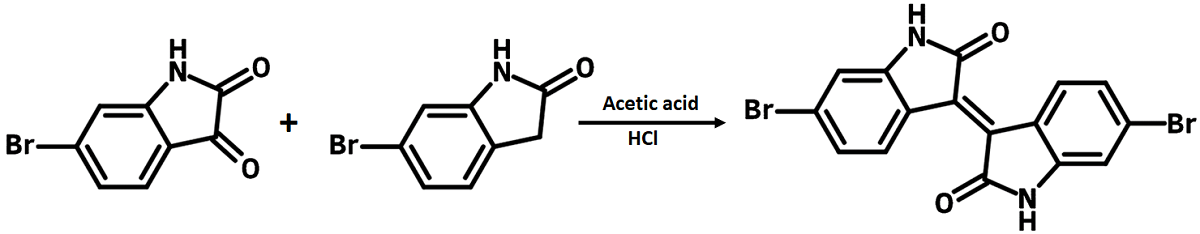
6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo can be prepared from a condensation reaction in acetic/hydrogen chloride acid between 6-Bromoindoline-2,3-dione and 6-Bromoindolin-2-one. Poly(isoindigo-alt-benzothiadiazole) (PIIG-BT), a copolymer alternating isoindigo and benzothiadiazole as the main backbone shows record high electron mobility of up to 0.22 cm2 V-1s-1.
General Information
| CAS Number | 1147124-21-7 |
| Chemical Formula | C16H8Br2N2O2 |
| Full Name | 6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo |
| Molecular Weight | 420.05 g/mol |
| Synonyms | 6-Bromo-3-(6-bromo-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one (E)-6,6'-Dibromo-[3,3'-biindolinylidene]-2,2'-dione |
| Classification / Family | Isoindigo, semiconductor synthesis intermediates, low band gap polymers, OLED, OFETs, organic photovoltaics |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Purity | >98% (by 1H NMR) |
| Melting Point | N/A |
| Appearance | Dark red/brown powder/crystals |
MSDS Documentation
 6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo MSDS sheet
6,6′-Dibromoisoindigo MSDS sheet
Literature and Reviews
-
Acceptor–acceptor type isoindigo-based copolymers for high-performance n-channel field-effect transistors, G. Kim et al., Chem. Commun., 50, 2180-2183 (2014); 10.1039/C3CC48013E.
-
Synthesis of N,N′-dialkyl-6,6′-dibromoisoindigo Derivatives by Continuous Flow, V. Maes et al., J. Flow Chem., 5(4), 201–209 (2015); DOI: 10.1556/1846.2015.00033 DOI: 10.1556/1846.2015.00033.
-
Chlorination as a useful method to modulate conjugated polymers: balanced and ambient-stable ambipolar high-performance field-effect transistors and inverters based on chlorinated isoindigo polymers, T. Lei et al., Chem. Sci., 4, 2447-2452 (2013); 10.1039/C3SC50245G.
