BPBPA
CAS Number 164724-35-0
Charge Transport Layer Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Hole Transport Layer Materials, Materials,An Electron-Rich Triarylamine Derivative
Widely used as hole transport layer in OLEDs and solar cells, N,N,N',N'-Tetra(4-biphenylyl)-4,4'-biphenyldiamine, CAS No. 164724-35-0, Sublimed ≥99.0%
BPBPA is a benzidine derivative with two amines substituted by four biphenyl groups. It demonstrates high charge carrier mobility of 1.74 ×10−2 cm2/V⋅s, enabling rapid hole-extraction from the adjacent donor layer. This results in an enhanced open-circuit voltage and leads to an improvement of powder conversion efficiency (PCE) of 9% with reference devices.
BPBPA is commonly used as a hole transport layer (HTL) material in OLEDs. The molecule has a highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) energy value at −5.5 eV and a lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy value at −2.0 eV. The work function of BPBPA conveniently matches with other materials, making it suitable as a reference HTL in the investigation of high-efficiency fluorescent emitters.
Hole transport material
Applied in OLEDs and solar cells
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
High carge carrier mobility
1.74 ×10−2 cm2/V⋅s
Sublimed grade purity
>99.5% Grade purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 164724-35-0 |
|---|---|
| Full Name | N,N,N',N'-Tetra(4-biphenylyl)-4,4'-biphenyldiamine |
| Chemical Formula | C60H44N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 793.03 g/mol |
| Purity | Sublimed >99.5% (HPLC) |
| Charge Carrier Mobility | μ = 1.74 × 10−2 cm2/V⋅s [1] |
| HOMO/LUMO |
HOMO = −5.5 eV LUMO = −2.0 eV [1] |
| Melting Point | Tm = 265 °C |
| Appearance | Off-white powder |
| Synonyms | N,N,N',N'-Tetrakis(4-biphenylyl)benzidine, N4,N4,N4',N4'-Tetra[(1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl]-(1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diamine, N,N'-Tetra(4-biphenyl)benzidine, 4-Phenyl-n-(4-phenylphenyl)-N-[4-[4-(4-phenyl-N-(4-phenylphenyl)anilino)phenyl]phenyl]aniline, TBB, TBBDA |
| Classification or Family | Hole transport layers, Hole extraction materials, Sublimed materials, Semiconducting molecules, Benzidines, OLEDs, Solar cells |
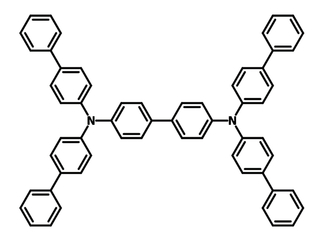
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device Structure | ITO (50 nm)/BPBPA (30%):HATCN (40 nm)/BPBPA (10 nm)/TNPA (10 nm)/a-ADN:IDCz-2DPA (5%) (30 nm)/TNPT (5 nm)/ZADN (20 nm)/LiF(1.5 nm)/Al (200 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Color |
|
| External Quantum Efficiency | 5.6% |
| Current Efficiency | 6.4 cd/A |
| Maximum Luminance | 47600 cd/cm-2 |
| Turn On Voltage | 3.0 V |
| Device Structure | ITO/DNTPD (60 nm)/BPBPA (20 nm)/PCzAC (10 nm)/mCBP:PTZ-TRZ(30 nm)/DBF-Trz (5 nm)/ZADN (30 nm)/LiF:Al [5] |
|---|---|
| Color |
|
| External Quantum Efficiency | 13% |
| Current Efficiency | 42 cd/A |
| Power Efficiency | 20 lm/W |
| Voltage at 200 cd/cm-2 | 2.53 V |
*For chemical structure information, please refer to the cited references.
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- High mobility hole extraction material for organic solar cell application, G. Kim et al., Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 565 (1), 14–21 (2012); DOI: 10.1080/15421406.2012.690989.
- A novel fluorene–indolocarbazole hybrid chromophore to assemble high efficiency deep-blue fluorescent emitters with extended device lifetime, V. Patil et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 8, 3051 (2020); DOI: 10.1039/c9tc06434f.
- Isomeric fused benzocarbazole as a chromophore for blue fluorescent organic light-emitting diodes, V. Patil et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 8, 8320 (2020); DOI: 10.1039/d0tc01268h.
