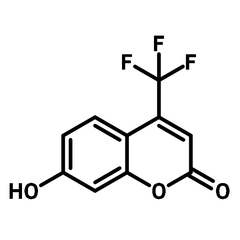
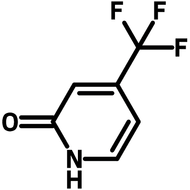
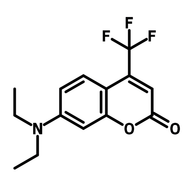
7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin
CAS Number 575-03-1
Chemistry Building Blocks, Fluorinated Building Blocks, Heterocyclic Building Blocks, Monomers
A fluorinated coumarin derived building block
Used as a synthesis intermediate for dyes in applications of DSSCs, OLEDs and sensors
7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin (CAS number 575-03-1), derived from coumarin, is a pyrone fused benzene heterocyclic compound with a hydroxy group at 7-position and a trifluoromethyl substituent at 4-position. By having the electron delocalised core, 7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin is widely used as dyes and emitters in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) and OLEDs. 7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin has a strong binding affinity with H2S/HS−. The fluorescence intensity of 7-hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin increases after the binding activity, which makes it a chemical sensor for detecting H2S/HS−. The photosensitivity of 7-hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin is not limited to a specific chemical, but also related to the medium microviscosity and polarity. It allows 7-hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin to be uses in monitoring chemical reactions such as polymerization.
7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin has also shown the theoretical possibility of proton transfer/proton shuttling under excitation, based on the change of photoacidity.
Multiple functional groups
For facile synthesis
Fluorinated coumarin building block
For drug discovery, solar cells, and OLEDs
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
High purity
>98% High purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 575-03-1 |
| Chemical Formula | C10H5F3O3 |
| Full Name | 7-Hydroxy-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin |
| Molecular Weight | 230.14 g/mol |
| Synonyms | 4-(Trifluoromethyl)umbelliferone, 7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2H-chromen-2-one |
| Classification / Family | Fluorinated building block, Heterocyclic building block, Dyes, DSSCs, OLED, Sensors |
Chemical Structure

Product Details
| Purity | 98% |
| Melting Point | Tm = 178 °C – 180 °C |
| Appearance | Pale purple powder |
MSDS Documentation
 7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin MSDS Sheet
7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin MSDS Sheet
Literature and Reviews
-
A tyrosinase fluorescent probe with large Stokes shift and high fluorescence enhancement for effective identification of liver cancer cells, Q. Sun et al., Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 285, 12183(2023); DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2022.121831.
-
4-Trifluoromethyl-substituted coumarins with large stokes shifts: synthesis, bioconjugates, and their use in super-resolution fluorescence microscopy, H. Schill et al., Chem. Eur. J., 19, 16556-16565(2013); DOI: 10.1002/chem.201302037.
-
Concerted electron-proton transfer in the optical excitation of hydrogen-bonded dyes, B. Westlake et al., PNAS, 108, 21(2011); DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1104811108.
-
Mechanism of interaction of coumarin-based fluorescent molecular probes with polymerizing medium during free radical polymerization of a monomer, I. Kamińska et al., Polym. Test., 55, 310-317(2016); DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2016.09.013.
-
Intermolecular proton shuttling in excited state proton transfer reaction: insights from theory, M. Savarese et al., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 16, 8661-8666(2014); DOI: 10.1039/C4CP00068D.
- The synthesis, crystal, hydrogen sulfide detection and cell assement of novel chemsensors based on coumarin derivatives, Y. Chen et al., Sci. Rep., 8, 16159(2018); DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34331-9.
Related Products
We stock a wide range of monomers available to purchase online. Please contact us if you cannot find what you are looking for.
![2-Ethylhexyl 4,6-dibromo-3-fluorothieno[3,4-b]thiophene-2-carboxylate](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/ptb7-monomer-b361-ossila-chemical-structure.png?v=1648818400&width=190)
![2,5-bis(trimethylstannyl)-thieno[3,2-b]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/2_5-bis-trimethylstannyl-thieno-3_2-b-thiophene_structure.jpg?v=1504193831&width=190)
![2,6-dibromo-4,4-bis(2-ethylhexyl)-4H-cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,4-b']dithiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/4Hcyclopentadithiophene.jpg?v=1431610575&width=190)
![2,7-Dibromo-9,9-bis[3,3'-(N,N-dimethylamino)-propyl]fluorene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/dibromo-fluorene-diyl-bisdimethylpropan-amine.jpg?v=1431610994&width=190)
![3,6-bis(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2,5-bis(2-octyldodecyl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/bisbromothiophenyl-bisoctyldodecylpyrrolo-dione.jpg?v=1431611190&width=190)
![4H-Cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,4-b']dithiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/cyclopentadithiophene_12a14774-f96a-4ebc-a0d0-2c5483da9180.jpg?v=1445441165&width=190)
![Benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']dithiophene-4,8-dione](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/benzo-dithiophene-dione.jpg?v=1437904702&width=190)
![Thienothiophene, Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/thienothiophene.jpg?v=1431611114&width=190)
![Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene-2-carbonitrile](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/thienothiophene-2-carbonitrile.jpg?v=1439548051&width=190)
![DTT, Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/dtt-chemical-structure.png?v=1653477307&width=190)
![3,6-Dibromothieno[3,2-b]thiophene (TT36)](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/3-6-dibromothienothiophene-chemical-structure.png?v=1653663075&width=190)
![2,3,5,6-Tetrabromothieno[3,2-b]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Tetrabromo-thienothiophene-chemical-structure.png?v=1665673773&width=190)
![2,6-Dibromodithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Dibromodithienothiophene-chemical-structure.png?v=1666702461&width=190)
![2,5-Dihydro-3,6-di-2-thienyl-pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/2_5-Dihydro-3_6-di-2-thienyl-pyrrolo_3_4-c_pyrrole-1_4-dione-chemical-structure-dpp.png?v=1667321819&width=190)
![6,9-bis(5-bromo-4-(2-butyloctyl)thiophen-2-yl)dithieno[3,2-f:2',3'-h]quinoxaline](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/bisbromo-butyloctylthiophenyl-dithienoquinoxaline-chemical-structure.png?v=1669202898&width=190)
![Indolo[3,2-b]carbazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Indolocarbazole-chemical-structure.png?v=1670495077&width=190)
![10,15-Dihydro-5H-diindolo[3,2-a:3',2'-c]carbazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Dihydro-diindolocarbazole-chemical-structure.png?v=1670502109&width=190)
![Indolo[2,3-a]carbazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/indolo-2-3-a-carbazole-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1678288567&width=190)
![2,2-Bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]propane (BAPP)](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/bapp-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1679403349&width=190)
![2,2'-Dimethyl[1,1'-biphenyl]-4,4'-diamine](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/2-2-dimethyl1-1-biphenyl-4-4-diamine-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1680597662&width=190)
![2,2-Bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]hexafluoropropane (4-BDAF)](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/4-bdaf-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1681225583&width=190)
![1-[2-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]imidazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/files/1-2-trifluoromethylphenylimidazole-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1682593257&width=190)