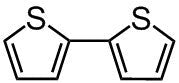
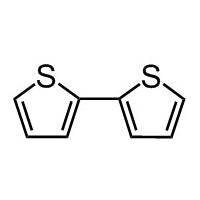
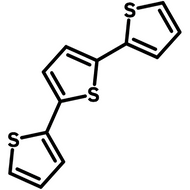
2,2'-bithiophene
CAS Number 492-97-7
Chemistry Building Blocks, Heterocyclic Building Blocks, Monomers
High purity 2,2'-bithiophene, for applications in organic electronics
For the synthesis of small molecules or polymer semiconductors
2,2'-bithiophene (CAS number 492-97-7) is an intermediate widely used for the synthesis of small molecules or polymer semiconductors in application of organic electronics. It has proven that 2,2'-bithiophene exists as a mixture of the cis-like and the trans-like planar structures. 5,5'-positions of 2,2'-bithiophene are easily accessible for bromination and stannylation to give 5,5'-dibromo-2,2'-bithiophene or 5,5'-trimethylstannyl-2,2'-bithiophene, which can be used for direct arylation reactions.
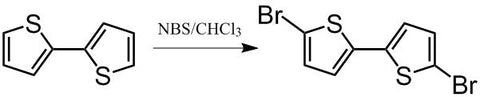
A synthesis precusor
For bithiophene backboned polymers
Bithiophene building block
For semiconductors, OFETs, and solar cells
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
High purity
>99% High purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 492-97-7 |
| Chemical Formula | C8H6S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 166.26 g/mol |
| Synonyms | 2,2′-Bithienyl, 2,2′-Dithienyl 2-(2-thienyl)thiophene 2-(thien-2-yl)thiophene |
| Classification / Family | Thiophene, Bithiophene, Heterocyclic five-membered ring, Organic materials, Semiconductor Synthesis, Low band gap polymers, OFETs, Organic Photovoltaics, Polymer Solar Cells |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Purity | 99% |
| Melting Point | 32 °C - 33 °C |
| Appearance | Yellowish liquid/solid |
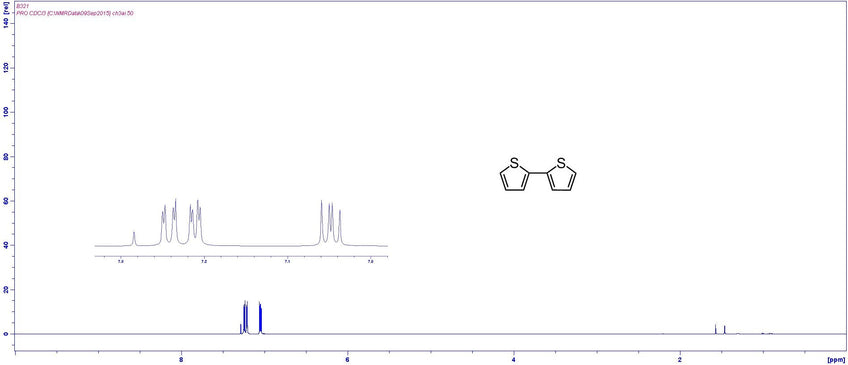
Characterisation by 1H-NMR (example)
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- White light from an electroluminescent diode made from poly[3(4‐octylphenyl)‐2,2’‐bithiophene] and an oxadiazole derivative, M. Berggren et al, J. Appl. Phys. 76, 7530 (1994); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.357984.
- Electronic structure of thiophene and pyrrole dimers: 2,2’‐bithiophene, 2,2’‐thienylpyrrole, and 2,2’‐bipyrrole, D. Birnbaum et al., J. Chem. Phys. 95, 4783 (1991); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.461721.
- Highly Efficient Light-Harvesting Ruthenium Sensitizer for Thin-Film Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells, C-Y. Chen et al., ACS Nano, 3 (10), 3103–3109 (2009); DOI: 10.1021/nn900756s.
- 3,6-Di(furan-2-yl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione and bithiophene copolymer with rather disordered chain orientation showing high mobility in organic thin film transistors, Y. Li et al., J. Mater. Chem., 21, 10829-10835 (2011).
- Indolo[3,2-b]carbazole-based alternating donor–acceptor copolymers: synthesis, properties and photovoltaic application, E. Zhou et al., J. Mater. Chem., 19, 7730-7737 (2009).
- A Binaphthyl–Bithiophene Copolymer for Light Emitting Devices, Y. Li et al., Macromol. Chem. Phys., 203, 37–40 (2002).
- A high-mobility electron-transporting polymer for printed transistors, H. Yan et al., nature, 457, 679 (2009).
Related Products
We stock a wide range of monomers available to purchase online. Please contact us if you cannot find what you are looking for.
 2,2'-bithiophene MSDS sheet
2,2'-bithiophene MSDS sheet
![2-Ethylhexyl 4,6-dibromo-3-fluorothieno[3,4-b]thiophene-2-carboxylate](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/ptb7-monomer-b361-ossila-chemical-structure.png?v=1648818400&width=190)
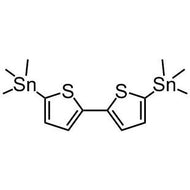
![2,5-bis(trimethylstannyl)-thieno[3,2-b]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/2_5-bis-trimethylstannyl-thieno-3_2-b-thiophene_structure.jpg?v=1504193831&width=190)
![2,6-dibromo-4,4-bis(2-ethylhexyl)-4H-cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,4-b']dithiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/4Hcyclopentadithiophene.jpg?v=1431610575&width=190)
![2,7-Dibromo-9,9-bis[3,3'-(N,N-dimethylamino)-propyl]fluorene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/dibromo-fluorene-diyl-bisdimethylpropan-amine.jpg?v=1431610994&width=190)
![3,6-bis(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2,5-bis(2-octyldodecyl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/bisbromothiophenyl-bisoctyldodecylpyrrolo-dione.jpg?v=1431611190&width=190)
![4H-Cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,4-b']dithiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/cyclopentadithiophene_12a14774-f96a-4ebc-a0d0-2c5483da9180.jpg?v=1445441165&width=190)
![Benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']dithiophene-4,8-dione](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/benzo-dithiophene-dione.jpg?v=1437904702&width=190)
![Thienothiophene, Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/thienothiophene.jpg?v=1431611114&width=190)
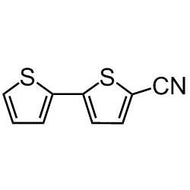
![Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene-2-carbonitrile](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/thienothiophene-2-carbonitrile.jpg?v=1439548051&width=190)
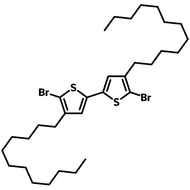
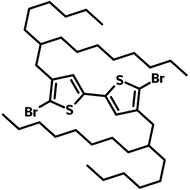
![DTT, Dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/dtt-chemical-structure.png?v=1653477307&width=190)
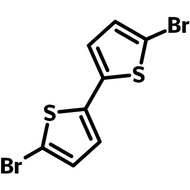
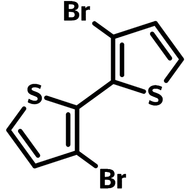
![3,6-Dibromothieno[3,2-b]thiophene (TT36)](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/3-6-dibromothienothiophene-chemical-structure.png?v=1653663075&width=190)
![2,3,5,6-Tetrabromothieno[3,2-b]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Tetrabromo-thienothiophene-chemical-structure.png?v=1665673773&width=190)
![2,6-Dibromodithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Dibromodithienothiophene-chemical-structure.png?v=1666702461&width=190)
![2,5-Dihydro-3,6-di-2-thienyl-pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/2_5-Dihydro-3_6-di-2-thienyl-pyrrolo_3_4-c_pyrrole-1_4-dione-chemical-structure-dpp.png?v=1667321819&width=190)
![6,9-bis(5-bromo-4-(2-butyloctyl)thiophen-2-yl)dithieno[3,2-f:2',3'-h]quinoxaline](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/bisbromo-butyloctylthiophenyl-dithienoquinoxaline-chemical-structure.png?v=1669202898&width=190)
![Indolo[3,2-b]carbazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Indolocarbazole-chemical-structure.png?v=1670495077&width=190)
![10,15-Dihydro-5H-diindolo[3,2-a:3',2'-c]carbazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/Dihydro-diindolocarbazole-chemical-structure.png?v=1670502109&width=190)
![Indolo[2,3-a]carbazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/indolo-2-3-a-carbazole-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1678288567&width=190)
![2,2-Bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]propane (BAPP)](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/bapp-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1679403349&width=190)
![2,2'-Dimethyl[1,1'-biphenyl]-4,4'-diamine](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/2-2-dimethyl1-1-biphenyl-4-4-diamine-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1680597662&width=190)
![2,2-Bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]hexafluoropropane (4-BDAF)](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/products/4-bdaf-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1681225583&width=190)
![1-[2-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]imidazole](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/files/1-2-trifluoromethylphenylimidazole-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1682593257&width=190)