PEDOT:PSS and PEDOT Based Polymers

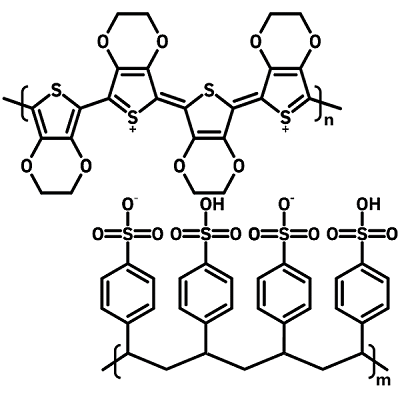
PEDOT:PSS (or Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate, CAS 155090-83-8) is a transparent conductive polymer. It is a mixture of the ionomer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), carrying positive charges, and polystyrene sulfonate, carrying negative charges. Due to its unique combination of conductivity, transparency, ductility, and ease of processing, PEDOT:PSS has become a benchmark material in thin-film electronic fabrication. There are many types of PEDOT dispersions, including PEDOT:PSS AI 4083 and PEDOT:PSS PH 1000.
In organic light emitting diodes, organic photovoltaics, and perovskite photovoltaics, PEDOT:PSS can be used as an interfacial layer for hole transport. It can also be used as a replacement for transparent conductors such as ITO or FTO. Commonly, it is used in applications where the underlying substrate is flexible.
The properties of PEDOT:PSS vary between dispersions, hence its versatility. The key properties of PEDOT:PSS are its conductivity and the size of its work function. Since PEDOT is conductive and PSS is insulating, the conductivity of the resulting polymer depends on the ratio between the two ionomers and the microstructure of the film. Similarly, a higher presence of PSS at the surface will result in a deeper work function.
PEDOT:PSS is typically available as a water-based emulsion. It is created via the polymerization of PEDOT monomers in a polystyrene sulfonic acid solution. We supply all our PEDOT:PSS solutions in light resistant bottles with temperature indicators.
Jump to: PEDOT Materials | Choose the Right PEDOT | Frequently Asked Questions | Resources and Support
PEDOT Materials
Filter by solvent:
Filter by sheet resistance:
Filter by deposition method:
Filter by applications:
PEDOT:PSS from Ossila was featured in the high-impact paper (IF 30.85), A Wearable Supercapacitor Based on Conductive PEDOT:PSS-Coated Cloth and a Sweat Electrolyte, L. Manjakkal et al., Adv. Mater., 1907254 (2020); DOI: 10.1002/adma.201907254.
Choose the Right PEDOT

Choosing the right PEDOT product for you could be a difficult task. Each has a different base solvent, conductivity, viscosity, and even composition. At Ossila, we have a range of PEDOT:PSS and PEDOT:Complex products. They are available in different solvents for applications in OLED, OPV, and sensors, and are suitable for different deposition methods, i.e. spin coating, inkjet printing and screen printing.
PEDOT Products by Sheet Resistance
| 100-1000 / Ω/sq | 1000 - 10E4 / Ω/sq | 10E4 - 10E6 / Ω/sq | +10E6 / Ω/sq |
|---|---|---|---|
PEDOT Products by Application
| OLED | OPV | Transistors | Sensor | Transparent Electrodes | Conductive Textile and Fabric | LC Writing Boards |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
PEDOT Products by Solvent Base
| Water | Toluene | Anisole | Butyl benzoate | Glycols (Paste) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTL Solar 4 | S V4 STAB | ||||
PEDOT Products by Deposition Method
|
Coating
(Spin coating, spray coating, slot die coating, doctor-blade coating, dip coating) |
Inkjet Printing | Screen Printing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P JET (OLED) | S V4 STAB | ||
Frequently Asked Questions
How Should PEDOT Materials be Stored?
The recommended storage temperature of PEDOT:PSS and PEDOT dispersions is between 5 and 10 °C. It is recommended that you store the dispersion at the front of a refrigerator. The product is not usable if frozen, so should be kept away from the back of the refrigerator.
The dispersions can tolerate up to a week outside of the refrigerator (e.g. during shipping) without negative consequences for the PEDOT:PSS performance. Over time at elevated temperatures, the PEDOT:PSS can phase separate, aggregate, and form a solid that drops to the bottom of the bottle, reducing performance. Brief heating to a maximum of 50 °C has no adverse effect on product properties.
What is the Shelf Life of PEDOT Materials?
When stored at 5 to 10 °C, the PEDOT dispersion will give you consistent performance over 12 months if used regularly. The official recommended shelf life from the manufacturer is 9 months after production if the dispersion is never used or disturbed. After this time, the dispersion will gradually separate or sediment at a very slow rate, resulting in lower concentrations and thinner films.
Material degradation is mitigated by frequent use of the dispersion due to the gentle agitation when decanting. Through constant use, it is possible to use a single bottle of PEDOT:PSS for many years without harming device performance.
Resources and Support
Deposition
Applications
Literature
Efficient organometal trihalide perovskite planar-heterojunction solar cells on flexible polymer substrates, H. J. Snaith et. al. Nature Communications, 4, (2013) DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3761
High efficiency stable inverted perovskite solar cells without current hysteresis, M. Grätzel et. al. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, (2015) 2725-2733 DOI: 10.1039/c5ee00645g